Fluoroquinolone-induced generalised fixed drug eruption: a rare clinical image
Sreeprada Bollineni, Gaurang Aurangabadkar
Corresponding author: Gaurang Aurangabadkar, Department of Respiratory Medicine, Datta Meghe Medical College, Nagpur, India 
Received: 23 Aug 2024 - Accepted: 13 Oct 2024 - Published: 18 Feb 2025
Domain: Pulmonology
Keywords: Fluoroquinolones, atypical pneumonia, drug eruptions
©Sreeprada Bollineni et al. Pan African Medical Journal (ISSN: 1937-8688). This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution International 4.0 License (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
Cite this article: Sreeprada Bollineni et al. Fluoroquinolone-induced generalised fixed drug eruption: a rare clinical image. Pan African Medical Journal. 2025;50:56. [doi: 10.11604/pamj.2025.50.56.45087]
Available online at: https://www.panafrican-med-journal.com//content/article/50/56/full
Images in clinical medicine 
Fluoroquinolone-induced generalised fixed drug eruption: a rare clinical image
Fluoroquinolone-induced generalised fixed drug eruption: a rare clinical image
&Corresponding author
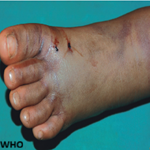
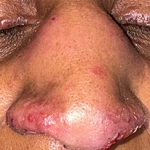
Fluoroquinolones are commonly used as antimicrobial agents in patients presenting with respiratory diseases with levofloxacin, ofloxacin, and moxifloxacin, and have a significant role in the management of pulmonary tuberculosis and atypical pneumonia. However, the use of fluoroquinolones is also associated with the development of adverse drug reactions such as tendon rupture, Qtc interval prolongation, and generalised drug eruptions. Here, we present a 70-year-old male patient who presented with generalised drug eruption rash over the body 3 days after starting levofloxacin therapy for atypical pneumonia. The patient was treated as per the dermatologist's advice with oral corticosteroids and antihistamines. After 7 days, significant improvement was noted in skin eruptions. This clinical image aims to highlight a rare adverse effect of a commonly used antimicrobial agent.
Figure 1: multiple lesions of generalised drug eruption in a patient treated with levofloxacin