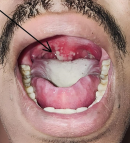
A clinical presentation of herpangina with ulcerative lesion over uvula
Pawan Banduji Itankar, Gaurav Rajendra Sawarkar
Corresponding author: Pawan Banduji Itankar, Department of Rachana Sharir, Mahatma Gandhi Ayurved College Hospital and Research Centre, Datta Meghe Institute of Higher Education and Research (Deemed to be University) Salod (H), Wardha, India 
Received: 08 Mar 2024 - Accepted: 15 Jul 2024 - Published: 24 Jul 2024
Domain: Infectious disease
Keywords: Herpangina, ulcerative lesion, fever
©Pawan Banduji Itankar et al. Pan African Medical Journal (ISSN: 1937-8688). This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution International 4.0 License (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
Cite this article: Pawan Banduji Itankar et al. A clinical presentation of herpangina with ulcerative lesion over uvula. Pan African Medical Journal. 2024;48:133. [doi: 10.11604/pamj.2024.48.133.43209]
Available online at: https://www.panafrican-med-journal.com//content/article/48/133/full
A clinical presentation of herpangina with ulcerative lesion over uvula
&Corresponding author
A 23-year-old male patient came to the outpatient department (OPD) with complaints of an ulcerative lesion over the uvula, fever, headache, and throat pain for 3 to 4 days, and no past medical history. He took antibiotics (azithromycin) and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) (paracetamol+ibuprofen) for three days after taking NSAIDs only the pain subsided but didn´t get relief from the ulcerative lesion. Therefore, an antiviral (Acicylovir) prescribed for five days helps to relieve associated symptoms, and the ulcerative lesion healed completely. Enteroviruses (i.e group A coxsackie virus) are the source of the viral infection known as herpangina, which often strikes children under the age of ten years; though it can strike anybody at any age depending on the immunity of an individual and is seen during autumn and summer season for 7 to 10 days. Clinically, it is an acute self-limiting tiny ulcerative or vesicular lesion in the posterior oropharynx, uvula, and throat region accompanied by an intense fever associated with headache and loss of appetite. Uses of antibiotics are ineffective in such conditions.
Figure 1: ulcerative or vesicular lesion over uvula