Interest of hepatic steatosis index (HSI) in screening for metabolic steatopathy in patients with type 2 diabetes
Halima Fennoun, Souhaila El Mansouri, Mohammed Tahiri, Nassim Essabah Haraj, Siham El Aziz, Fouad Hadad, Wafaa Hliwa, Wafaa Badr, Asma Chadli
Corresponding author: Asma Chadli, Endocrinology, Diabetology and Metabolic Disease Department Ibn Rochd, University Hospital of Casablanca, Casablanca, Morocco 
Received: 15 Jul 2020 - Accepted: 07 Sep 2020 - Published: 25 Nov 2020
Domain: Endocrinology,Hepatology
Keywords: Metabolic, steatopathy, diabetes, screening, HSI score, transaminases, liver ultrasound
©Halima Fennoun et al. Pan African Medical Journal (ISSN: 1937-8688). This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution International 4.0 License (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
Cite this article: Halima Fennoun et al. Interest of hepatic steatosis index (HSI) in screening for metabolic steatopathy in patients with type 2 diabetes. Pan African Medical Journal. 2020;37:270. [doi: 10.11604/pamj.2020.37.270.25007]
Available online at: https://www.panafrican-med-journal.com//content/article/37/270/full
Research 
Interest of hepatic steatosis index (HSI) in screening for metabolic steatopathy in patients with type 2 diabetes
Interest of hepatic steatosis index (HSI) in screening for metabolic steatopathy in patients with type 2 diabetes
Halima Fennoun1, Souhaila El Mansouri2, Mohammed Tahiri2, Nassim Essabah Haraj1, Siham El Aziz1, Fouad Hadad2, Wafaa Hliwa2, Wafaa Badr2, Asma Chadli1,&
&Corresponding author
Introduction: metabolic steatopathy or non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is frequently associated with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) with an increased risk of progression to advanced fibrosis. The purpose of our study was to determine the interest of hepatic steatosis index (HSI) in the detection of hepatic steatosis in patients with type 2 diabetes in order to establish an appropriate screening program of this disease in our population.
Methods: cross-sectional study involving 281 type 2 diabetics hospitalized in the Department of Endocrinology in collaboration with the hepato-gastroenterology department at the University Hospital Ibn Rochd Casablanca between January 2018 and June 2018. Anthropometric variables studied were, biological, hepatic steatosis index (HSI) and liver ultrasound. The HSI score of> 36 predicted the presence of fatty liver. The HSI score (fatty liver index) was calculated for all patients using the following formula: 8 × (ALT / AST) + BMI + 2 (if type 2 diabetes) + 2 (if female). Statistical analysis was performed with SPSS Version 19 software. The sensitivity and the specificity of the HSI score were calculated by 2x2 contingency table. The area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUROC) was also analyzed.
Results: average age of patients was 54.15 ± 13.14 years with a female predominance (76.9% of cases), and a sex ratio of 3.32. Mean duration of diabetes of 10.5 ± 8.03 years with an average glycated hemoglobin of 10.23 ± 1.96%. BMI was 29.53 ± 4.55 kg/m², the average waist circumference was 99.51 ± 10.98 cm. 39.1% of patients were hypertensive, 58% were dyslipidemic. Abnormalities in transaminases were found in 6% of patients. Prevalence of NAFLD was 45.2% based on the HSI score > 36. This prevalence is consistent with the findings made by the liver ultrasound (47.7% of cases). Hepatic steatosis was significantly correlated with dyslipidemia (P=0.006), overweight (P=0.00015), obesity (P=0.001) and hypertriglyceridemia (P=0.0003). The sensitivity of HSI was 89.55%, negative predictive value (NPV) was 90.91%, specificity was 95.24%, and positive predictive value (PPV) was 94.49%. AUROC for HSI was at 0.979 (95% CI, 0.962-0.997).
Conclusion: hepatic steatosis is common among our patients; it is correlated with dyslipidemia, obesity and hypertriglyceridemia.
Metabolic steatopathy is a global public health problem; it is the leading cause of chronic hepatopathies in Western countries. It encompasses several disorders ranging from simple hepatic steatosis to nonalcoholic fatty liver hepatitis (NASH), fibrosis and liver cirrhosis. Its association with type 2 diabetes is common [1]. Indeed, it is estimated that about 62%, or two-thirds of type 2 diabetes are hepatic steatosis and 20 to 30% of patients with diabetes are hepatic steatosis [2,3]. Metabolic fatty liver is associated with a high risk of morbidity and mortality related to liver damage severity of imposing early detection to prevent these complications. HSI is a non-invasive marker to identify patients at high risk of fatty liver. The objective of this study is to determine the value of non-invasive score HSI in screening for hepatic steatosis in patients with type 2 diabetes in order to establish an appropriate screening program of this disease in our population.
This is a cross-sectional study involving 281 type 2 diabetics hospitalized in the Department of Endocrinology in collaboration with the hepato-gastroenterology department at the University Hospital Ibn Rochd Casablanca between January 2018 and June 2018. The study included any unknown type 2 diabetic patients followed for chronic hepatopathy, or notion of taking hepatotoxic drugs nor alcohol abuse. The variables were studied: age, sex, duration of diabetes, diabetes treatment, glycemic control, cardiovascular risk factors associated with the laboratory tests and liver ultrasound. The HSI score (Hepatic steatosis index) was calculated in all patients using the following formula: 8×(ALT / AST) + BMI + 2 (if type 2 diabetes) + 2 (if female). HSI score of > 36 predicted the presence of hepatic steatosis. Data collection is based on a detailed operating record. For statistical analysis, SPSS version 19 was used. The sensitivity and the specificity of the HSI score were calculated by contingency table. The area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUROC) was also analyzed.
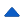
The prevalence of NAFLD was 45.2% based on the HSI score > 36. It is consistent with the findings made by the liver ultrasound (47.7% of cases). The average age of patients was 54.15 ± 13.14 years with a female predominance (76.9% of cases) and a sex ratio of 3.32. The mean duration of diabetes was 10.5 ± 8.03 years with average glycated hemoglobin of 10.23 ± 1.96%. BMI was 29.53 ± 4.55 kg/m², the average waist circumference was 99.51 ± 10.98 cm. 39.1% of patients were hypertensive, 58% were dyslipidemic (Table 1). Abnormalities in transaminases were found in 6% of patients. Hepatic steatosis was significantly correlated with dyslipidemia (P=0.006), overweight (P=0.00015), obesity (P=0.001) and hypertriglyceridemia (P=0.0003). The Table 2 shows risk factors in diabetics with hepatic steatosis on ultrasound compared to those without hepatic steatosis. In multivariate analysis, the factor associated to hepatic steatosis was ALT (P=0.036, odds ratio: 1.143). The sensitivity of HSI was 89.55%, NPV was 90.91%, specificity was 95.24%, and PPV was 94.4% based on data of contingency table (Table 3). The AUROC for HSI was at 0.979 (95% CI, 0.962-0.997) (Figure 1).
Metabolic fatty liver disease is characterized by an abnormal accumulation of fat in hepatocytes. In the literature, its prevalence in type 2 diabetic patients is between 5 and 87% [4]. It is closely associated with the different components of the metabolic syndrome [5]. Hypertriglyceridemia is a risk factor of development of hepatic steatosis. In our study, hepatic steatosis was significantly correlated with obesity, dyslipidemia and hypertriglyceridemia. Although there is a correlation between fatty liver disease and transaminase levels, most patients with type 2 diabetes have normal serum transaminase levels despite higher liver fat content [5]. The increase in transaminases is not systematically related to the severity of liver disease [6-8]. According to the literature, including Mottin's study showed that 68% of diabetic patients with advanced steatosis have normal levels of transaminases [8,9]. In our patients, abnormal transaminases were objectified in more than 6% of cases. Patients with type 2 diabetes have a higher risk of developing NASH; a death related to fatty liver complications [10,11]. Adams found a twice as high risk of all-cause mortality in patients with T2DM [11]. Another study by Zoppini found similar results with three to five times higher deaths, mainly due to NAFLD [11]. These results suggest that screening for NAFLD should be considered in T2DM. The development of non-invasive serum markers of hepatic damage has facilitated the detection of patients at risk and the follow-up of patients with fatty liver [9]. Imaging may require the precise diagnosis of fatty liver disease, but cannot predict the stage of liver disease. A large cohort has shown a high prevalence of fatty liver disease in type 2 diabetic patients using non-invasive scores [10-12]. Hamaguchi used abdominal ultrasound to assess NAFLD, with a specificity of 100% and a sensitivity of 92% compared to the results of liver biopsy [13,14]. However, conventional imaging is too expensive for mass screening. The hepatic steatosis index is a simple non-invasive tool and a validated screening for NAFLD, with performance characterized by an AUROC of 0.81 (95% confidence interval 0.80-0.836) [15]. HSI score < 30 excludes hepatic steatosis. An HSI score > 36 confirms this with a sensitivity of 93% [15-18]. In our study, the sensitivity of HSI was 89.55%.
In our study, fatty liver disease was common in patients with type 2 diabetes with normal transaminases. Thus, hepatic steatosis should be screened for in type 2 diabetic patients regardless of their level of transaminases. The non-invasive HSI score is a simple, inexpensive screening for fatty liver, offering the possibility of early diagnosis and prevention of complications related to this condition, it should be part of liver monitoring in patients with type 2 diabetes.
What is known about this topic
- Metabolic steatopathy is a frequent and often asymptomatic in patients with type 2 diabetes;
- The HSI score is an easy and inexpensive tool offering mass screening for hepatic steatosis.
What this study adds
- The study reveals that HSI score may be used to facilitate mass screening for hepatic steatosis.
The authors declare no competing interests.
All authors conceived the study, participated in data analysis, and writing of the final manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Table 1: general clinical and biological characteristics of diabetic patients
Table 2: risk factors in diabetics with hepatic steatosis on ultrasound compared to those without hepatic steatosis
Table 3: number of patients according to result of HSI score and hepatic steatosis
Figure 1: ROC curve for the HSI score
- Trovato FM, Tognarelli JM, Crossey MM, Catalano D, Taylor-Robinson SD, Trovato GM. Challenges of liver cancer:Future emerging tools in imaging and urinary biomarkers. World J Hepatol. 2015;7:2664-75. PubMed | Google Scholar
- Wong WV, Vergniol J, Wong GL, Foucher J, Chan HL-Y, Le Bail B et al. Diagnosis of fibrosis and cirrhosis using liver stiffness measurement in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology. 2010;51(2):454-62. PubMed | Google Scholar
- Szczepaniak LS, Nurenberg P, Leonard D, Browning JD, Reingold JS, Grundy S et al. Magnetic resonance spectroscopy to measure hepatic triglyceride content:Prevalence of hepatic steatosis in the general population. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2005;288(2):462-8. PubMed | Google Scholar
- Pherson Mc, Stewart SF, Henderson E, Burt AD, Day CP. Simple noninvasive fibrosis scoring systems can reliably exclude advanced fibrosis in patients with non alcocholic fatty liver disease. Gut. 2010;59(9):1265 1269. PubMed | Google Scholar
- Singh A, Le P, Peerzada MM, Lopez R, Alkhouri N. The utility of Noninvasive scores in Assessing the prevalence of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and advanced in type 2 diabetic patients. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2018 Mar;52(3):268-272. PubMed | Google Scholar
- Targher G, Bertolini L, Rodella S, Tessari R, Zenari L, Lippi G et al. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease is independently associated with an increased incidence of cardiovascular events in type 2 diabetic patients. Diabetes Care. 2007;30:2119-21. PubMed | Google Scholar
- Targher G, Lonardo A, Byrne CD. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and chronic vascular complications of diabetes mellitus. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2018;14:99-114. PubMed | Google Scholar
- Mottin DC, MorettoM, Padoin AV, Swarowsky AM, Toneto MG, Glock L et al. The role of ultrasound in the diagnosis of hepatic steatosis in morbidly obese patients. ObesSurg. 2004;14:635-7. PubMed | Google Scholar
- Jornayvaz EN, Samuel VT, Shulman GI. The role of muscle insulin resistance in the pathogenesis of atherogenic dyslipidemia and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease associated with the metabolic syndrome. AnnuRevNutr. 2010;30:273-90. PubMed | Google Scholar
- Fracanzani AL, Valenti L, Bugianesi E, Andreoletti M, Colli A, Vanni E et al. Risk of severe liver disease in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease with normal aminotransferase levels:a role for insulin resistance and diabetes. Hepatology. 2008;48(3):792-8. PubMed | Google Scholar
- Drescher HK, Weiskirchen S, Weiskirchen R. Current Status in Testing for nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH). Cells. 2019;8(8). PubMed | Google Scholar
- Adams THE, Harmsen S, Save JL, Enders FB, Therneau T, Angulo P. A non-alcoholic fatty liver disease increases the risk of death in patients with diabetes:cohort study based on community. Am J Gastroenterol. 2010;105:1567-1573. PubMed | Google Scholar
- Zoppini G, Fedeli U, Gennaro N, Saugo Mr, Targher G, Bonora E. Mortality from chronic liver disease related to diabetes. Am J Gastroenterol. 2014;109:1020-1025. PubMed | Google Scholar
- Hamaguchi Mr, Kojima T, Itoh Y, Harano Y, Fujii k, Nakajima T et al. The severity of ultrasonography Findings in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease Reflects the metabolic syndrome and visceral fat accumulation. Am J Gastroenterol. 2007;102:2708-15. PubMed | Google Scholar
- Tiikkainen M, Hakkinen AM, Korsheninnikova E, Nyman T, Mäkimattila S, Yki-Järvinen H et al. Effects of rosiglitazone and metformin is pleased liver fat, hepatic insulin resistance, insulin clearance, and gene expression in adipose tissue in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes. 2004;53:2169-76. PubMed | Google Scholar
- Musso G, Gambino R, Cassader M, Pagano G. A meta-analysis of randomized trials for the treatment of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology. 2010;52:79-104. PubMed | Google Scholar
- Mazhar SM, Shiehmorteza M, Sirlin CB. Noninvasive assessment of hepatic steatosis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2009;7:135-40. PubMed | Google Scholar
- Li H, Fang Q, Gao F, Fan J, Zhou J, Wang X et al. Fibroblast growth factor 21 levels are Increased in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease patients and are correlated with hepatic triglyceride. J Hepatol. 2010;53:934-40. PubMed | Google Scholar