Monoarthrite du genou révélatrice d’une arthropathie tabétique
Zeineb Alaya, Walid Osman
Corresponding author: Zeineb Alaya, Service de Rhumatologie, Hôpital Farhat Hached, avenue Ibn El Jazzar, 4000, Sousse, Tunisie 
Received: 12 Jan 2017 - Accepted: 21 Jan 2017 - Published: 30 Jan 2017
Domain: Radiology,Infectious disease,Rheumatology
Keywords: Arthrite, genou, tabès, scanner
©Zeineb Alaya et al. Pan African Medical Journal (ISSN: 1937-8688). This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution International 4.0 License (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
Cite this article: Zeineb Alaya et al. Monoarthrite du genou révélatrice d’une arthropathie tabétique. Pan African Medical Journal. 2017;26:39. [doi: 10.11604/pamj.2017.26.39.11634]
Available online at: https://www.panafrican-med-journal.com//content/article/26/39/full
Monoarthrite du genou révélatrice d’une arthropathie tabétique
Knee monoarthritis revealing tabetic arthropathy
Zeineb Alaya1,&, Walid Osman2
1Service de Rhumatologie, Hôpital Farhat Hached, Sousse, Tunisie, 2Service d’Orthopédie, Hôpital Sahloul, Sousse, Tunisie
&Auteur correspondant
Zeineb Alaya, Service de Rhumatologie, Hôpital Farhat Hached, avenue Ibn El Jazzar, 4000, Sousse, Tunisie
We here report the case of a 53-year old patient presenting with right knee monoarthritis evolving for 6 months without fever associated with an biologic inflammatory syndrome. Articular puncture collected sterile inflammatory fluid. Front and lateral radiographs of the knee ( A and B) and CT scan of the knee (C and) showed internal femoral condyle destruction with osteolysis of the medial border of the internal tibial tray associated with multiple bone constructions with intra-articular fragments, intra-articular effusion and thickening of the synovium. The diagnosis of hypertrophic tabetic arthropathy was retained on the basis of a 20-year history of syphilitic inoculation chancre, posterior radiculo-cordonal syndrome, imaging data and positive syphilitic serology (TPHA-VDRL) result on a sample of blood and CSF. The patient was treated with penicillin G (24 million units/day) for 15 days. More common in men than in women, tabes, which has become exceptional, is diagnosed late around 50 to 60 years. Tabetic arthropathy is a destructive neurogenic disease secondary to treponemal infection. It affects 4 to 10% of tabetic patients. The most often affected joint is the knee. Primary forms are often misunderstood and mimic common type of knee osteoarthritis. It is usually hypertrophic. Treatment is essentially medical based on penicillin G.
Key words: Arthritis, knee, tabes, CT scan
Il s’agit d’un patient âgé de 53 ans, qui a consulté pour une monoarthrite du genou droit évoluant depuis 6 mois sans fièvre, associé à un syndrome inflammatoire biologique. La ponction articulaire a ramené un liquide inflammatoire stérile. Les radiographies du genou de face ( A) et de profil (B) et la TDM du genou (C et D) ont montré une destruction du condyle fémoral interne avec une ostéolyse du rebord médial du plateau tibial interne associé à de multiples constructions osseuses avec présence de fragments intra-articulaires, d’un épanchement intra-articulaire et d’un épaississement de la synoviale. Le diagnostic d'arthropathie tabétique dans sa forme hypertrophique a été retenu devant un antécédent de chancre d’inoculation syphilitique datant de 20 ans, un syndrome radiculocordonal postérieur, les données de l’imagerie et une sérologie syphilitique (TPHA-VDRL) positive dans le sang et le LCR. Le patient a été traité par pénicilline G (24 millions/j) pendant 15 jours. Plus fréquent chez l'homme que chez la femme, le tabès, devenu exceptionnel, se découvre tardivement vers 50 ou 60 ans. L'arthropathie tabétique est une affection neurogène destructrice secondaire à l'infection par le tréponème. Elle concerne 4 à 10% des tabétiques. Le genou est l'articulation la plus souvent atteinte. Les formes de début souvent méconnues miment une gonarthrose banale. L'aspect habituel réalise une forme hypertrophique. Le traitement de l'arthropathie tabétique est essentiellement médical basé sur la pénicilline G.
Figure 1: (A,B) radiographie du genou droit de face et de profil: destruction du condyle fémoral interne avec ostéolyse du plateau tibial interne associé à de multiples constructions osseuses; (C,D) scanner du genou droit en coupe sagittale et axiale: destruction du condyle fémoral interne avec ostéolyse du rebord médial du plateau tibial interne associé à de multiples constructions osseuses avec présence de fragments intra-articulaires, d’un épanchement intra-articulaire et d’un épaississement de la synoviale
Search
This article authors
On Pubmed
On Google Scholar
Citation [Download]
Navigate this article
Similar articles in
Key words
Tables and figures
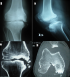 Figure 1: (A,B) radiographie du genou droit de face et de profil: destruction du condyle fémoral interne avec ostéolyse du plateau tibial interne associé à de multiples constructions osseuses; (C,D) scanner du genou droit en coupe sagittale et axiale: destruction du condyle fémoral interne avec ostéolyse du rebord médial du plateau tibial interne associé à de multiples constructions osseuses avec présence de fragments intra-articulaires, d´un épanchement intra-articulaire et d´un épaississement de la synoviale
Figure 1: (A,B) radiographie du genou droit de face et de profil: destruction du condyle fémoral interne avec ostéolyse du plateau tibial interne associé à de multiples constructions osseuses; (C,D) scanner du genou droit en coupe sagittale et axiale: destruction du condyle fémoral interne avec ostéolyse du rebord médial du plateau tibial interne associé à de multiples constructions osseuses avec présence de fragments intra-articulaires, d´un épanchement intra-articulaire et d´un épaississement de la synoviale











