Dermatose flagellée induite par bléomycine: un nouveau cas clinique
Salmi Narimane, Hassan Errihani
Corresponding author: Salmi Narimane, Service d’Oncologie Médicale, Institut National d’Oncologie, Rabat, Maroc 
Received: 04 May 2016 - Accepted: 12 May 2016 - Published: 17 Oct 2016
Domain: Clinical medicine
Keywords: Erythème flagellé, BEP, bleomycine
©Salmi Narimane et al. Pan African Medical Journal (ISSN: 1937-8688). This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution International 4.0 License (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
Cite this article: Salmi Narimane et al. Dermatose flagellée induite par bléomycine: un nouveau cas clinique. Pan African Medical Journal. 2016;25:86. [doi: 10.11604/pamj.2016.25.86.9784]
Available online at: https://www.panafrican-med-journal.com//content/article/25/86/full
Dermatose flagellée induite par bléomycine: un nouveau cas clinique
Bleomycin induced flagellate dermatitis: a new clinical case
Salmi Narimane1,&, Hassan Errihani1
1Service d’Oncologie Médicale, Institut National d’Oncologie, Rabat, Maroc
&Auteur correspondant
Salmi Narimane, Service d’Oncologie Médicale, Institut National d’Oncologie, Rabat, Maroc
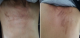
We report the case of a 56-year old female patient with granulosa tumour of the ovary treated in our institute. She underwent complete resection followed by auxiliary chemotherapy according to BEP protocol (Bleomycine 30 Mg J1, J8 and J15, Etoposide 100mg/m2 J1-J5, Cisplatine 20 mg/m2 J1-J5). After her second cycle of BEP regimen, the patient had multiple skin linear hyperpigmentations at the level of the superior anterior and posterior thoracic regions and of the lower back, without pruritus, resembling Bleomycin- induced flagellate erythema. These skin lesions occurred despite the use of antihistamine premedication and persisted after treatment discontinuation. Flagellate rash also known as flagellate dermatitis is a complication of Bleomycine therapy in 20% to 30% of cases. Generally, this toxicity occurs after a cumulative dose of 90-285 mg, but some cases were reported at doses of 15 mg. This is a benign disease whose occurrence should not put the continuation of Bleomycin therapy at risk.
Key words: Flagellate erythema, BEP, bleomycin
Nous rapportons le cas d’une patiente âgée de 56 ans, suivie dans notre institut pour une tumeur de granulosa de l’ovaire ayant reçu une chirurgie complète suivie d’une chimiothérapie adjuvante selon le protocole BEP (Bléomycine dose totale de 30 mg à J1, J8 et J15, Etoposide 100mg/m2 de J1 à J5, Cisplatine 20mg/m2 de J1 à J5). Après sa 2ème cure de BEP, la patiente a présenté plusieurs hyperpigmentations linéaires cutanées au niveau de l’étage supérieur des régions thoraciques antérieure et postérieure ainsi qu’au niveau du bas du dos, sans notion de prurit, correspondant à l’érythème flagellé induit par la Bleomycine. Ces lésions cutanées sont apparues malgré l’utilisation d’une prémédication par antihistaminique et ont persisté après arrêt du traitement. L’érythème flagellé appelé, aussi dermatose flagellée, complique un traitement par Bleomycine dans 20% à 30% des cas. Généralement, cette toxicité survient après une dose cumulative de 90 à 285 mg, mais certains cas ont été reportés à partir des doses de 15 mg. C’est une pathologie bénigne dont l’apparition ne doit pas compromettre la poursuite de la Bleomycine.
Figure 1: pigmentations linéaires cutanées correspondant à une dermatose flagellée induite par la bleomycine