Electrocardiogrammes d´un patient COVID-19 traité par l´association hydroxychloroquine et azithromycine
Mohamed Elghali Benouna, Amine Ech-chenbouli
Corresponding author: Amine Ech-chenbouli, Département de Cardiologie, Rue des hôpitaux, CHU IbN Rochd, Casablanca, Maroc 
Received: 31 May 2020 - Accepted: 31 May 2020 - Published: 14 Jul 2020
Domain: Cardiology
Keywords: COVID-19, hydroxychlroquine, azithromycine
This article is published as part of the supplement PAMJ Special issue on COVID - 19 in Africa, commissioned by The Pan African Medical Journal.
©Mohamed Elghali Benouna et al. Pan African Medical Journal (ISSN: 1937-8688). This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution International 4.0 License (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
Cite this article: Mohamed Elghali Benouna et al. Electrocardiogrammes d´un patient COVID-19 traité par l´association hydroxychloroquine et azithromycine. Pan African Medical Journal. 2020;35(2):112. [doi: 10.11604/pamj.supp.2020.35.2.23878]
Available online at: https://www.panafrican-med-journal.com//content/series/35/2/112/full
Images in clinical medicine 
Electrocardiogrammes d´un patient COVID-19 traité par l´association hydroxychloroquine et azithromycine
Electrocardiogrammes d´un patient COVID-19 traité par l´association hydroxychloroquine et azithromycine
ECG changes in a patient with COVID-19 treated with hydroxychloroquine and azithromycin
Mohamed Elghali Benouna1, Amine Ech-chenbouli1,&
&Auteur correspondant
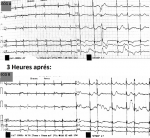
The study involved a 73-year old patient admitted to our hospital with moderate COVID-19 infection detected during acute coronary syndrome. The patient underwent revascularization using stenting of the circumflex artery eight hours after onset of chest pain. The patient had a history of type 2 diabetes treated with Metformin and high blood pressure treated with perindopril. At first he underwent ECG showing QTc level of 420 ms (corrected according to Bazett’s formula). He received hydroxychloroquine 200 mg three times a day and azithromycin 500 mg/day according to Moroccan COVID-19 treatment protocol in addition to his post-infarct treatment (Clopidogrel 1 tablet of 75 mg once a day; aspirin 1 tablet of 75 mg once a day; atorvastatin 1 tablet of 80 mg once a day, bisoprolol 2.5 mg/day. On the 5th day of his hospitalization daily ECG monitoring showed QT interval prolongation of 547 ms (corrected according to Bazett’s formula) with ventricular extrasystole (ECG A) justifying discontinuation of hydroxychloroquine/azithromycin treatment. Three hours after, another ECG was performed which showed focal atrial tachycardia with variable conduction and unchanged QTc (ECG B). No hydroelectrolyte imbalance associated with serum potassium 4.1 mmol/l and magnesemia 22mmol/l was detected. Outcome was favorable with QT returning to normal values, patient’s transition to paroxysmal atrial fibrillation requiring oral anticoagulation therapy and discharge after 21 days of hospitalization.
Key words: COVID-19, hydroxychlroquine, azithromycine
Un patient de 73 ans a été admis dans notre hôpital pour prise en charge d´une forme modérée d´infection au COVID-19 découverte au décours d´un syndrome coronaire aigu revascularisé par un stent de la Circonflexe à 8h de la douleur thoracique. Il avait comme antécédent un diabète de type 2 sous Metformine et une hypertension artérielle sous Périndopril. Après un ECG initial montrant un Qt (corrigé selon la formule de Bazett) à 420ms, le patient a été mis sous hydroxychloroquine 200mg x3/j et azithromycine 500mg/j conformément au Protocol marocain de traitement des patient COVID-19 en plus de son traitement post infarctus: clopidogrel 75mg 1cp/j; aspirine 75mg 1cp/j; atorvastatine 80mg 1cp/j, bisoprolol 2.5 mg/j. Au 5e jour de son hospitalisation il a présenté sur l'ECG quotidien de surveillance un prolongement du QT (corrigé selon la formule de Bazett) devenu à 547 ms avec une extrasystole ventriculaire (ECG A) justifiant l'arrêt de l'association hydroxychloroquine/ azithromycine. Trois heures après un autre ECG a objectivé le passage en tachyatriale focale à conduction variable avec un QTc inchangé (ECG B). Il n´y avait pas de troubles hydro électrolytique associés avec une kaliémie à 4.1 mmol/l et une magnésémie à 22mmol/l. L´évolution a été favorable avec retour du QT aux normes et passage du patient en fibrillation auriculaire paroxystique nécessitant une anticoagulation orale et une sortie du patient au bout de 21 jours d´hospitalisation.
Figure 1: electrocardiogramme 12 dérivations objectivant un Qt allongé et extrasystole ventriculaire (A) tachycardie atriale focale (B)
Search
This article authors
On Pubmed
On Google Scholar
Citation [Download]
Navigate this article
Similar articles in
Key words
Tables and figures
This supplement
- Clinical presentation, case management and outcomes for the first 32 COVID-19 patients in Nigeria (Accessed 18958 times)
- COVID-19 and the Nigerian child: the time to act is now (Accessed 17894 times)
- Profil clinique, biologique et radiologique des patients Algériens hospitalisés pour COVID-19: données préliminaires (Accessed 10355 times)
- The COVID-19 pandemic and social distancing in Nigeria: ignorance or defiance (Accessed 6430 times)
- Knowledge, risk perception and preparedness towards coronavirus disease-2019 (COVID-19) outbreak among Ghanaians: a quick online cross-sectional survey (Accessed 6234 times)
- Continuity of health service delivery during the COVID-19 pandemic: the role of digital health technologies in Uganda (Accessed 4205 times)
- Knowledge, risk perception and preparedness towards coronavirus disease-2019 (COVID-19) outbreak among Ghanaians: a quick online cross-sectional survey (Downloaded 868 times)
- Clinical presentation, case management and outcomes for the first 32 COVID-19 patients in Nigeria (Downloaded 611 times)
- The COVID-19 pandemic and social distancing in Nigeria: ignorance or defiance (Downloaded 601 times)
- Profil clinique, biologique et radiologique des patients Algériens hospitalisés pour COVID-19: données préliminaires (Downloaded 473 times)
- Continuity of health service delivery during the COVID-19 pandemic: the role of digital health technologies in Uganda (Downloaded 456 times)
- COVID-19 and the Nigerian child: the time to act is now (Downloaded 350 times)